Common Symptoms in TBI: Memory, concentration, decision making; slowness; headache; fatigability; confusion; mood vacillations; sleep problems; dizziness; balance problems; Increased sensitivity to light or sound; changes in vision, smell, taste; nausea; and ringing in the ears (Tinnutis) (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2003).
Incidence
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) affects 1.7 million people a year at a cost of 60 billion dollar a year in 2000 (CDC, 2008). The causes of TBI are
- falls (28%)
- motor vehicle accidents (20%)
- struck by/against events (19%) such as sports activities
- assaults (11%)
- blast injuries in the Iraq war (CDC, 2008)
QEEG example of a traumatic brain injury
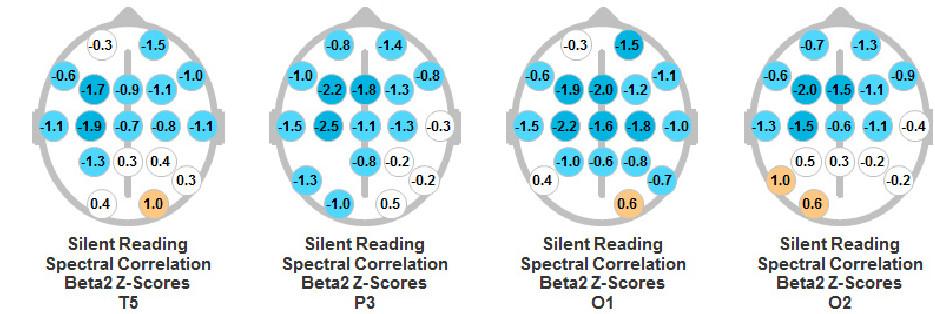
PB2=Phase beta2: CB2=Coherence Beta2: RPB2=Relative Power Beta2
The empty location represents the origin of a metaphorical flashlight which sends out a signal to the other locations. If the connection value is below normal (.50 standard deviations-SD) a blue color is filled for that circle. A darker blue is assigned to those values which are greater than 1.5 standard deviation below normative value. If the value is above the normative value, the color orange is employed. A darker orange color is employed for those values which are greater than 1.5 SD above the norm. The numbers in the circles represent the standard deviation value for the individual. The first row of head figures present the coherence and phase alpha relations during an auditory memory task.
